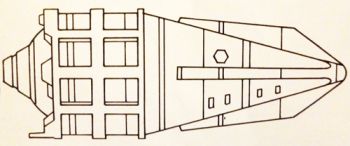
The Glenn class "space bus" entered service in 2060, and served as the principal surface-to-orbit carriers during the second half of the 21st century. More than 200 were built to accommodate the increasingly heavy traffic between Earth, orbiting satellite cities, Mars, Venus, and the asteroid belt. Perhaps the most distinctive feature of the Glenn class was its adaptability. With convertible interiors, they could be used for both industrial transport and passenger service. The class was removed from service in 2096.[1]
Specifications
| 140m (Passenger Area: 38.4m)
|
| 56.5m (Passenger Area: 45m)
|
| 10 million kg
|
- Officers: 5
- Crew: 23
- Passengers: Up to 450
|
Performance
| 800 million km (Earth to asteroid belt)
|
| 175 million km/hour
|
| 20 hours (Earth to asteroid belt)
|
| SpaceOp Advanced Fusion Engine
|
| Frozen deuterium
|
FASA Timeline
The Glenn class "space bus" entered service in 2052, and served as the principal surface-to-orbit carriers during the second half of the 21st century. More than 200 were built to accommodate the increasingly heavy traffic between Earth, orbiting satellite cities, Mars, Venus, and the asteroid belt. Perhaps the most distinctive feature of the Glenn class was its adaptability. With convertible interiors, they could be used for both industrial transport and passenger service. The class was removed from service in 2073.[1]
Specifications
| 140m (Passenger Area: 38.4m)
|
| 56.5m (Passenger Area: 45m)
|
| 10 million kg
|
- Officers: 5
- Crew: 23
- Passengers: Up to 450
|
Performance
| 800 million km (Earth to asteroid belt)
|
| 175 million km/hour
|
| 20 hours (Earth to asteroid belt)
|
| SpaceOp Advanced Fusion Engine
|
| Frozen deuterium
|
References